Explain Summation in End Plate Potential
The end-plate membrane is electrically polarized the inside being negative with respect to the outside because of an uneven distribution of ions. With no ACh binding to its receptors at the motor end-plate no action potential is produced and muscle contraction cannot occur.
The result of summation of postsynaptic potentials is the overall change in the.

. The two types of postsynaptic potentials are EPSP and IPSP. Spatial summation is related to associating the activity of multiple inputs to a neuron with each other. End-plate potential EPP ACh receptors are chemically gated channels that open when ACh binds to them Na diffuses into the cell through the channels while a little K diffuses out Cell membrane briefly becomes less negative at the end plate region EPP is local but it does lead to the opening of voltage-gated ion channels in the.
Explain the differences between the types of graded potentials including ions involved. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron. Depending on the sum total of many individual inputs summation may or may not.
The end plate potential a graded potential and a change in ion permeability D. For our purposes postsynaptic potentials are measured in the dendrites and cell bodies. This is the stimulus that will make the skeletal cell contract.
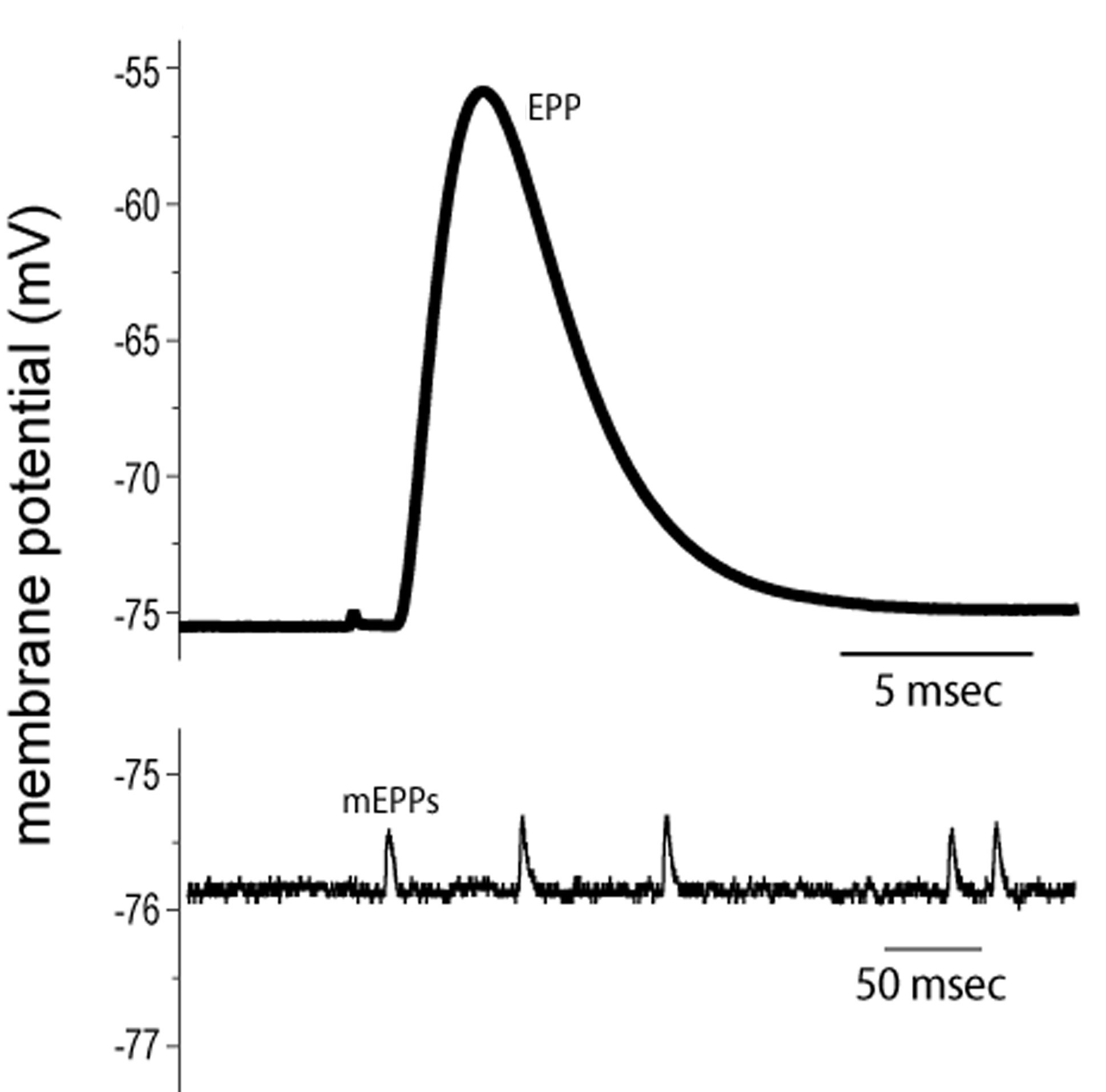
A depolarization caused by sodium ion movement into the cytosol. When a nerve impulse releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from the nerve terminal it binds to channel-shaped receptor molecules on the end plate opening the channels and allowing positively charged sodium ions. This effect can be seen in Figure 25 of Fatt and Katz 1951.
The shunting effect at the end-plate limits the peak depolarization of the action potential at this location to near the -15 mV reversal potential of the synaptic conductance increase of the postsynaptic membrane. Spatial and temporal summation can act together as well. The end-plate potential looks and behaves much like EPSPs in nerve cells.
Botulinum toxin prevents ACh from being released into the synaptic cleft. End-plate potential is produced. The summation of these IPSPs and the drop in membrane voltage will deviate away from the threshold potential inhibiting an action potential.
Its function is to transmit the electrical signal action potential from the nerve cell to the muscle cell. However these IPSPs and EPSPs may be occurring at the same time hence the postsynaptic neuron may be receiving excitatory signals from glutamate and inhibitory signals from GABA. The postsynaptic element is the motor end plate of the sarcolemma and the neurotransmitter is broken down by acetylcholinesterase.
If this end-plate poten-tial exceeds the threshold for activating Na channels an action potential results. They are called end plates because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large saucer-like appearance. The motor end-plate is the connection between the motor nerve and the skeletal muscle cell.
Temporal summation is the relationship of multiple action potentials from a single cell resulting in a significant change in the membrane potential. Generation of an action potential initiates the sequence of processes leading to contraction. End plate potentials are the voltages which cause depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction.
The ACh is rapidly inactivated by acetylcholinesterase an enzyme that is manufactured by the muscle cell and. This time includes diffusion of the acetylcholine the propagation of the muscle action potential release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum etc. Full relaxation of the muscle occurs and wave summation results E.
Ion channels that are opened by a. Botulinum toxin is produced by Clostridium botulinum a bacterium sometimes found in improperly canned foods. The different types of graded potentials are postsynaptic potentials pacemaker potentials receptor potentials end-plate potentials and slow-wave potentials.
A repolarization caused by sodium ion movement into the extracellular fluid. When wave summation occurs _____. Ingestion of very small amounts can cause botulism which.
Wave summation results and muscle twitches overlap. A repolarization caused by sodium ion movement into the cytosol. This is the time between the arrival of the action potential at the motor end-plate and the beginning of the contraction.
Summation which includes both spatial summation and temporal summation is the process that determines whether or not an action potential will be generated by the combined effects of excitatory and inhibitory signals both from multiple simultaneous inputs and from repeated inputs. A depolarization caused by sodium ion movement into the extracellular fluid. Postsynaptic potentials are changes in membrane potential that move the cell away from its resting state.
EPSP stands for the Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential and IPSP stands for the Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential. The end plate potential. The end-plate potential is.
If the preparation has been bathed in a solution containing the drug curare a substance used experimentally as a muscle relaxant and used by South American Indians as a poison that is applied to arrowheads the stimulus to the nerve leads to a change in potential called the end-plate potential. The muscle fiber has received a single stimulus event.

Human Physiology Chapter 12 Flashcards Quizlet

Endplate Potential All You Need To Know About Voltages That Cause Depolarization Of Skeletal Muscle Fibers Naija Super Fans
No comments for "Explain Summation in End Plate Potential"
Post a Comment